Meet the Toolkit
Prof. Maria Tackett
Topics
- Reproducible data analysis
- R and RStudio
- R Markdown
- Git and GitHub
Reproducible data analysis
Reproducibility checklist
Reproducibility checklist
Near-term goals
✔️ Are the tables and figures reproducible from the code and data?
✔️ Does the code actually do what you think it does?
✔️ In addition to what was done, is it clear why it was done?
Reproducibility checklist
Near-term goals
✔️ Are the tables and figures reproducible from the code and data?
✔️ Does the code actually do what you think it does?
✔️ In addition to what was done, is it clear why it was done?
Long-term goals
✔️ Can the code be used for other data?
✔️ Can you extend the code to do other things?
Toolkit
Scriptability → R
Literate programming (code, narrative, output in one place) → R Markdown
Version control → Git / GitHub
R and RStudio
What is R and RStudio?
R is a statistical programming language
RStudio is a convenient interface for R (an integrated development environment, IDE)
- At its simplest:*
- R is like a car’s engine
- RStudio is like a car’s dashboard
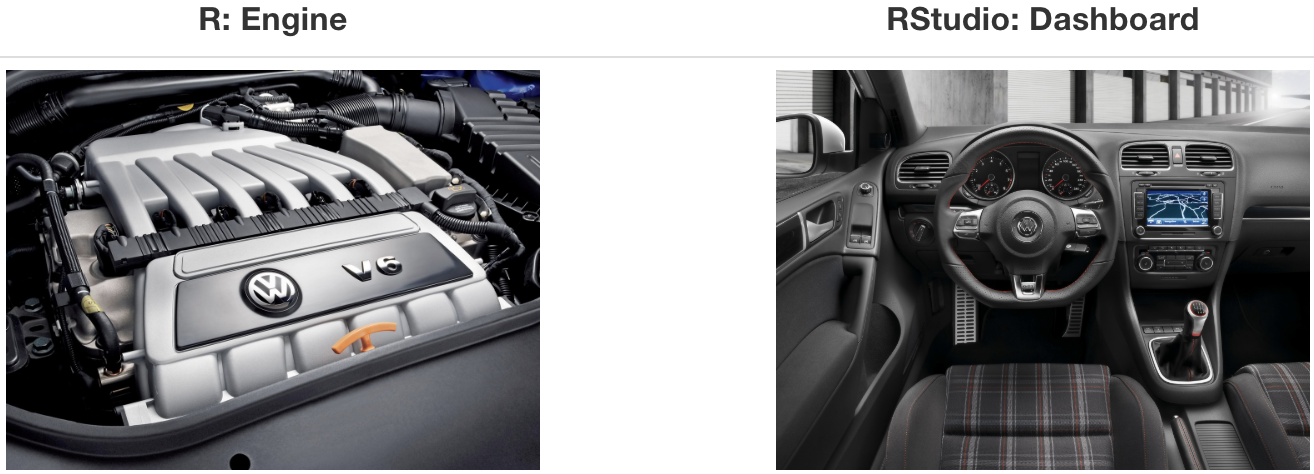

*Source: Modern Dive
R essentials (a short list)
- Functions are (most often) verbs, followed by what they will be applied to in parentheses:
do_this(to_this)do_that(to_this, to_that, with_those)R essentials (a short list)
- Functions are (most often) verbs, followed by what they will be applied to in parentheses:
do_this(to_this)do_that(to_this, to_that, with_those)- Columns (variables) in data frames are accessed with
$:
dataframe$var_nameR essentials (a short list)
- Functions are (most often) verbs, followed by what they will be applied to in parentheses:
do_this(to_this)do_that(to_this, to_that, with_those)- Columns (variables) in data frames are accessed with
$:
dataframe$var_name- Packages are installed with the
install.packagesfunction and loaded with thelibraryfunction, once per session:
install.packages("package_name")library(package_name)tidyverse

- The tidyverse is an opinionated collection of R packages designed for data science.
- All packages share an underlying philosophy and a common grammar.
Image from Teaching in the Tidyverse 2020
R Markdown
R Markdown
- Fully reproducible reports -- the analysis is run from the beginning each time you knit
- Simple Markdown syntax for text
- Code goes in chunks, defined by three backticks, narrative goes outside of chunks
How will we use R Markdown?
- Every assignment / lab / project / etc. is an R Markdown document
- You'll always have a template R Markdown document to start with
- The amount of scaffolding in the template will decrease over the semester
R Markdown tips
Resources
- R Markdown cheat sheet
- Markdown Quick Reference:
Help -> Markdown Quick Reference
R Markdown tips
Resources
- R Markdown cheat sheet
- Markdown Quick Reference:
Help -> Markdown Quick Reference
Remember: The workspace of the R Markdown document is separate from the console
Git and GitHub
Version control
We introduced GitHub as a platform for collaboration
But it's much more than that...
It's actually designed for version control
What is versioning?
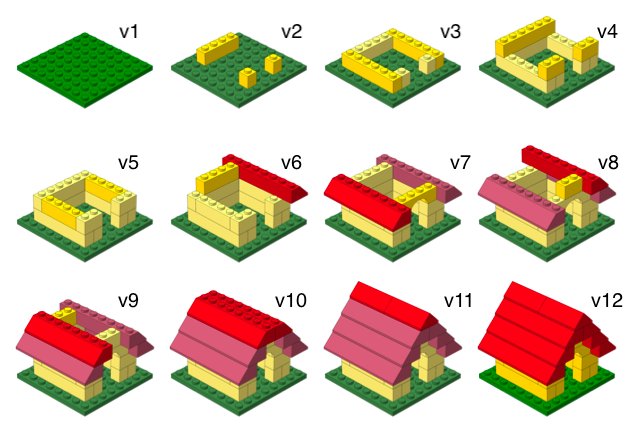
What is versioning?
with human readable messages
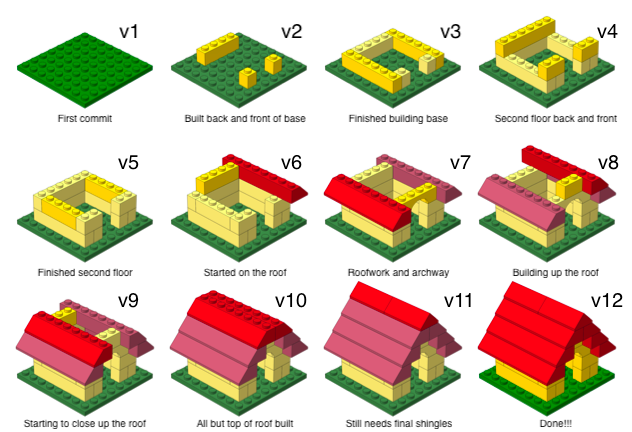
Why do we need version control?
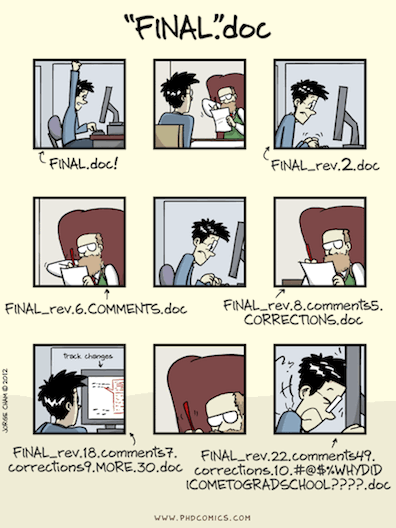


- Git is a version control system -- like “Track Changes” features from Microsoft Word.

Git is a version control system -- like “Track Changes” features from Microsoft Word.
GitHub is the home for your Git-based projects on the internet (like DropBox but much better).

Git is a version control system -- like “Track Changes” features from Microsoft Word.
GitHub is the home for your Git-based projects on the internet (like DropBox but much better).
There are a lot of Git commands and very few people know them all. 99% of the time you will use git to add, commit, push, and pull.
Git and GitHub tips
- We will be doing git things and interfacing with GitHub through RStudio
- If you Google for help, skip any methods for using git through the command line.
Git and GitHub tips
- We will be doing git things and interfacing with GitHub through RStudio
- If you Google for help, skip any methods for using git through the command line.
- There is a great resource for working with git and R: happygitwithr.com.
- Some of the content in there is beyond the scope of this course, but it's a good place to look for help.
Recap
Can you answer these questions?
- What is a reproducible data analysis, and why is it important?
- What is version control, and why is it important?
- What is R vs. RStudio?
- What is git vs. GitHub?